Best Describe the Properties of an Intramolecular Sn2 Reaction Mechanism
These solvents also act as nucleophiles. In the SN2 reaction the nucleophile attacks from the most δ region.

Complete Collection Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Notes Organic Chemistry Study
S N 2 is a kind of nucleophilic substitution reaction mechanism the name referring to the Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism.
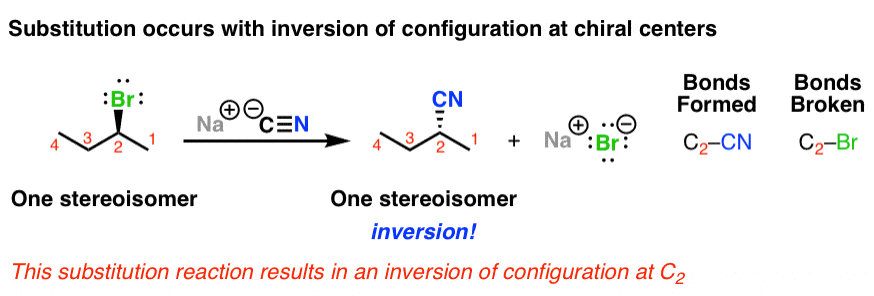
. 100 inversion of configuration at the reaction site not stereospecific bimolecular at rate-determining step unimolecular at rate-determining step first order second order rate is governed by steric effects rate is governed by the stability of the carbocation that. As a reminder from the introduction to nucleophilic substitutions these are reactions where the nucleophile replaces the leaving group. One in which the nucleophilic attack and the.
Different properties of SN² reactions. C bimolecular at rate-determining step. Intramolecular Sn2 reactions proceed rather readily and typically much faster than a competing intermolecular process if the reaction leads to a small ring 3-6 membered What is the intramolecular nucleophile in the case of diazotized amino acids.
This back-side attack causes an inversion study the previous slide. I GOC I SN2 I SN1. Answered Jul 3 2017 at 403.
-there will be a nucleophile and a molecule with a leaving group hence bimolecular. Select the statement that best describes the properties of an intramolecular SN2 reaction mechanism. Taking the hydrolysis of tertiary butyl bromide as an example the mechanism of the S N 1 reaction can be understood via the following steps.
Select the statements that best describe the properties of an intramolecular SN2 reaction mechanism. Important points for SN2 reactions. The S N 2 reaction is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistryIn this mechanism one bond is broken and one bond is formed synchronously ie in one step.
-The final goal of this type of reaction is to displace the leaving group LG with the nucleophile Nu. Examples of solvents used in S N 1 reactions include water and alcohols. This is because SN 2 reactions can occur primarily in two ways.
Intramolecular Diels-Alder occurs as well and while this is a single step its not exactly SN2 though as we saw in a past thread you can assign nucleoelectrophile designations to the dienedienophile. The term SN2 stands for Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular. The S N 2 reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where a bond is broken and another is formed synchronously.
Select the properties of the Sn2 reaction mechanism. These reactions are divided in two main types. In this post we will talk about the S N 2 mechanism of nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Rate is dependent on concentration and strength of Nucleophile. After the leaving group leaves the other substituents shift to make room for the newly-bonded nucleophile changing the stereochemistry of the molecule. Since two reacting species are involved in the slow rate.
What is Intramolecular SN2 reaction. The S N 2 Reaction Notes. The carbon-bromine bond is a polar covalent bond.
Alkyl halides in SN2 reactions. SN 2 reactions are stereospecific and can sometimes lead to a change in the stereochemical properties of the end product. - It is Single step reaction.
The carbon in the C-X bond will be partially positive and thus electrophilic. D unimolecular at rate-determining step. Select the statements that best describe the properties of an intramolecular SN2 reaction mechanism.
This does not cause any change in stereochemistry and the. Yes mechanism of this reaction involves internal attack. This is called a back-side attack.
In-depth discussion of SN2 reactions the mechanism itself and its properties. Transition state is formed which is sp² hybridized planar structure. 100 inversion of configuration at the reaction site not stereospecific bimolecular at rate-determining step unimolecular at rate-determining step first order second order rate is governed by steric effects rate is governed by the stability of the carbocation that.
These molecules react in solution. 100 inversion of configuration at the reaction site not stereospecific bimolecular at rate-determining step unimolecular at rate-determining step first order second order rate is governed by steric effects rate is governed by. Follow this answer to receive notifications.
Rate of reaction K R L Nu It is a second order reaction. 100 inversion of configuration at the reaction site. Behind the leaving group.
Select the statements that best describe the properties of an intramolecular Sn2 reaction mechanism. This problem has been solved. This type of reaction is also referred to as bimolecular nucleophilic.
I If the substance is an R enantiomer then in the SN 2 reaction the nucleophile will attack the substrate from the front end. Show activity on this post. S N 1 Reaction Mechanism.
Two reacting species are involved in the rate determining step of the reaction. For this to occur bonds must be broken and formed.
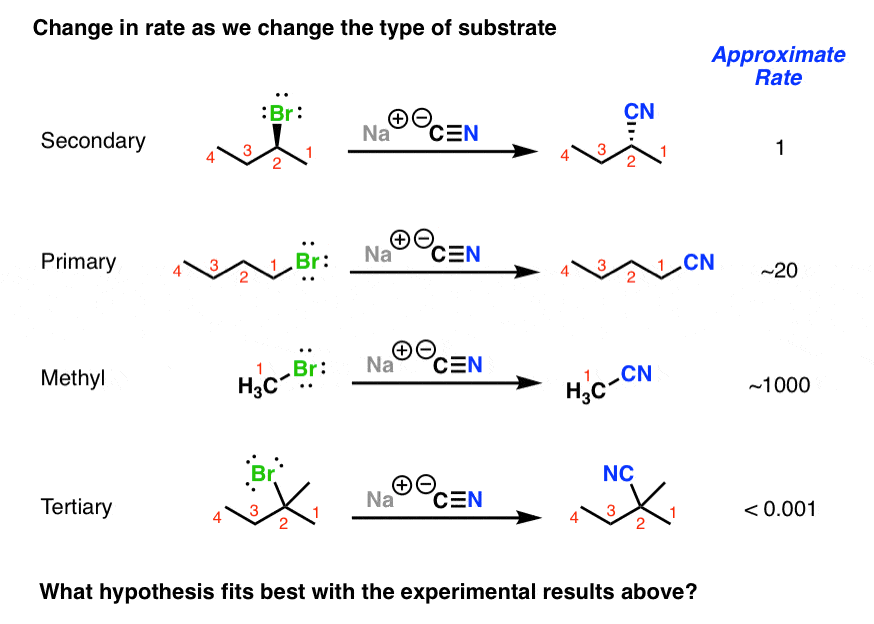
The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
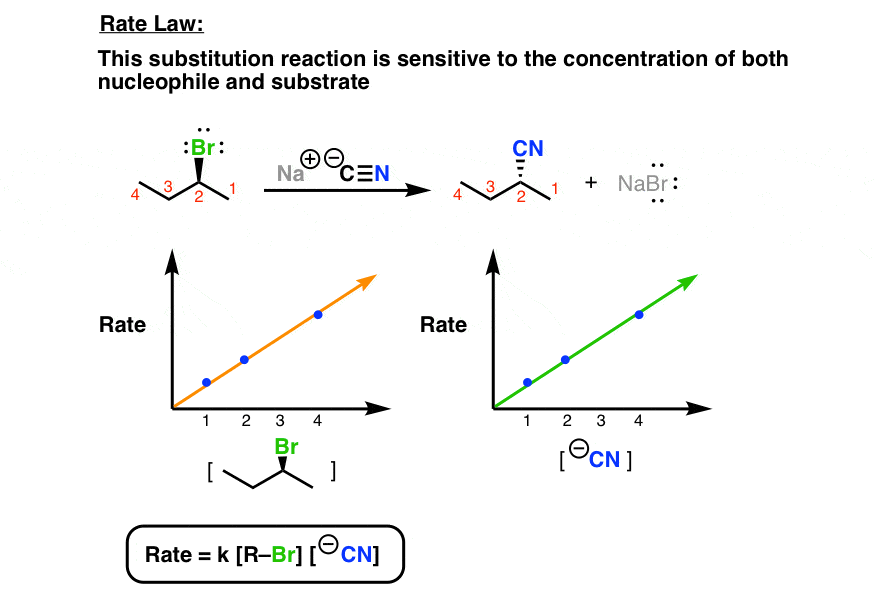
The Sn2 Reaction Mechanism Master Organic Chemistry
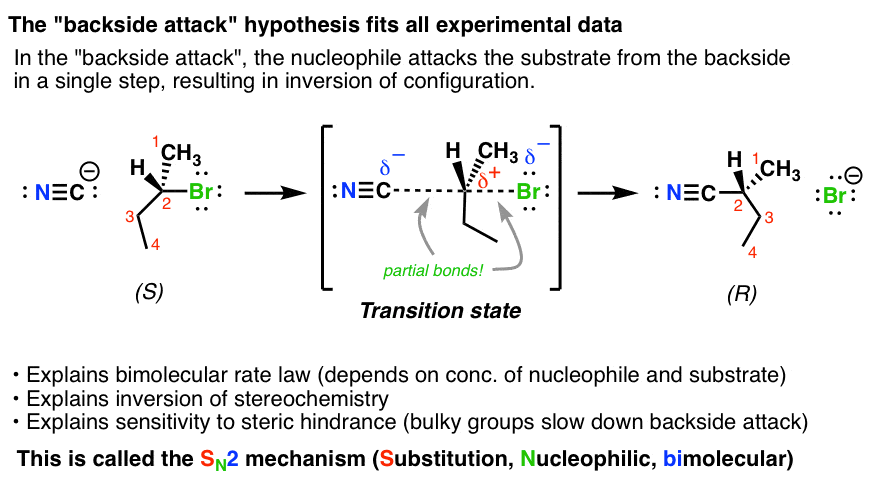
No comments for "Best Describe the Properties of an Intramolecular Sn2 Reaction Mechanism"
Post a Comment